With the crazy times we are in now, it has never been more important to WASH YOUR HANDS! But, have you ever wondered what’s going on when you do and how it works? We are going to give you a little crash coarse on how soap works since you have all this time (and germs) on your hands!
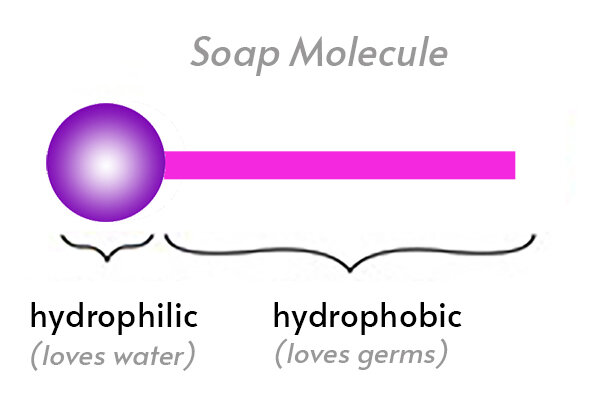
Soap, water, and oil/germs are all made up of molecules. Parts of these molecules are either hydrophobic or hydrophilic.
Hydrophilic, (hydro=water and philic=loving) these molecules are attracted to water and some molecules are Hydrophobic, (hydro=water and phobic=fearing), they are repelled by water.
Since we all know that water and oil do not mix, then we also know that hydrophilic and hydrophobic compounds do not mix.
Because of these properties, soap molecules for little safety bubbles called, micelles, which help trap germs and let them wash off your skin.
The oil-loving (hydrophobic) parts stick to the oil and trap oil in the center where it can't come into contact with the water.
Most of what we call germs which will not come off with just water. This is because germs are non-polar, which means they will not dissolve in the water so they need something to separate them from your hands.
Ever wonder why it is easier to clean dirty, greasy hands (and other things) in hot or warm water rather than cold water? It is because the fats and oils soften or melt in hot water, which allows them to attach more readily to the hydrophobic end of the soap molecule. In turn, that makes it easier to rinse away. So always use warm water!